Organizational Behavior: The Science of Group Interactions

What is Organizational Behavior and Why It Matters
Organizational behavior (OB) is the study of how individuals and groups interact within a workplace. It helps us understand the dynamics that affect employee performance, satisfaction, and overall organizational effectiveness. By analyzing these interactions, businesses can create a culture that promotes collaboration and innovation.
The ability to learn faster than your competitors may be the only sustainable competitive advantage.
Imagine a sports team: each player's behavior, attitudes, and communication styles influence the team's success. Similarly, in an organization, understanding these group dynamics can lead to better decision-making and improved morale. When employees feel valued and understood, they are more likely to contribute positively.
Ultimately, recognizing the importance of OB can help organizations foster an environment where people thrive, leading to higher productivity and lower turnover rates. This foundational understanding sets the stage for exploring specific dynamics within groups.
Key Theories in Organizational Behavior
There are several key theories in organizational behavior that provide insights into group interactions. For instance, Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs suggests that employees are motivated by a series of needs, from basic to complex. Understanding these needs can help managers create a supportive environment that nurtures individual and team growth.
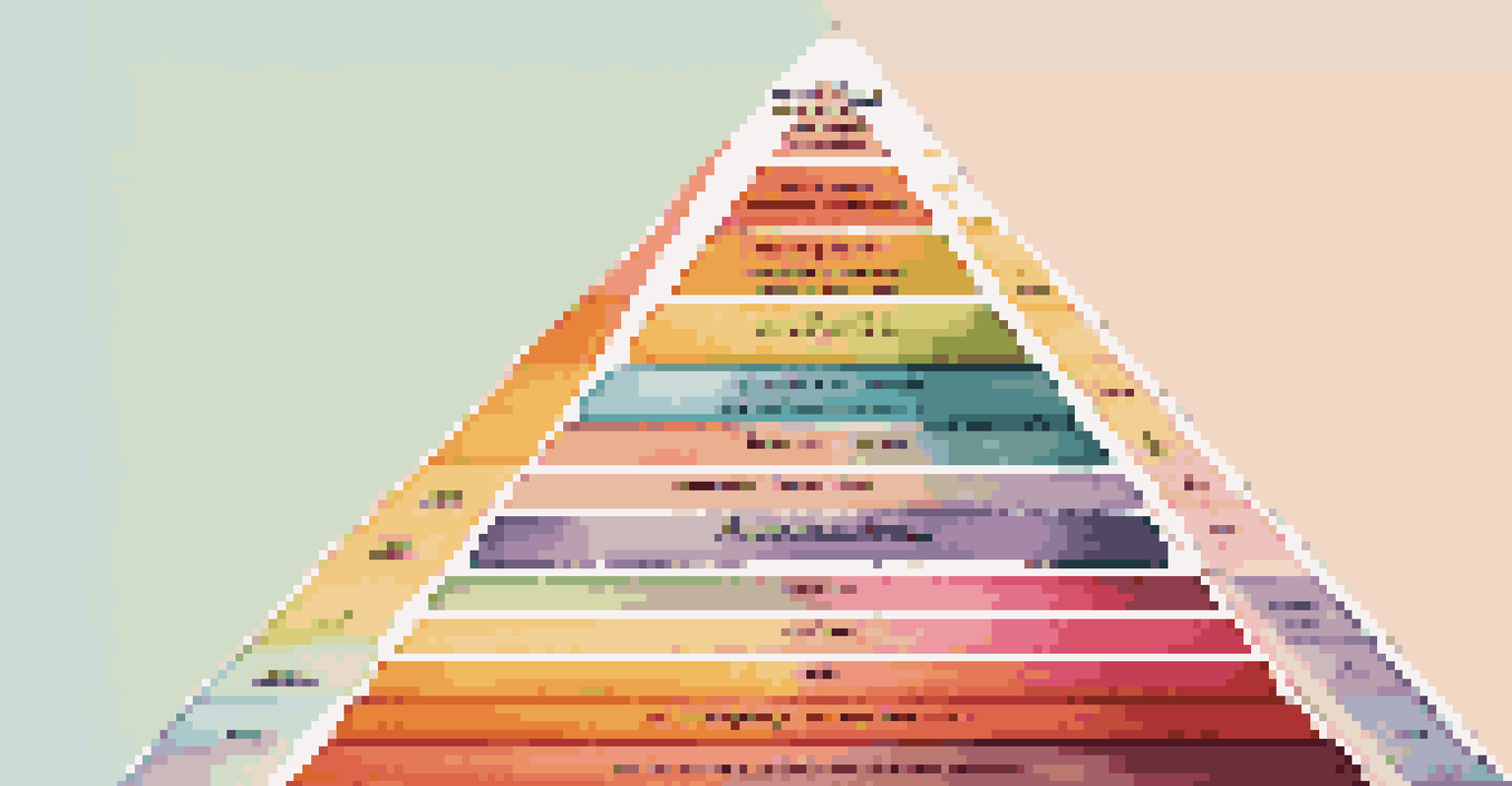
Another important theory is Herzberg's Two-Factor Theory, which distinguishes between hygiene factors (like salary and job security) and motivators (such as recognition and achievement). This differentiation helps organizations identify what truly drives employee engagement and satisfaction.
Understanding Organizational Behavior
Organizational behavior helps businesses improve employee performance and satisfaction through better understanding of group dynamics.
These theories are not just academic concepts; they can be applied practically to improve workplace culture. By implementing strategies based on these theories, organizations can enhance their overall effectiveness and employee well-being.
The Role of Communication in Group Dynamics
Effective communication is the backbone of successful organizational behavior. It ensures that team members are aligned on goals and understand their roles within the group. Poor communication can lead to misunderstandings, decreased morale, and conflicts, which can ultimately hinder productivity.
Communication works for those who work at it.
Consider a project team working on a tight deadline. If team members communicate openly, sharing their ideas and concerns, they are more likely to collaborate effectively and meet their objectives. On the other hand, if communication breaks down, it can lead to frustration and a lack of cohesion.
Therefore, fostering an environment that encourages open dialogue and feedback is crucial. Organizations that prioritize communication create a culture of trust, which enhances overall group dynamics.
The Impact of Leadership Styles on Group Behavior
Leadership styles significantly influence how groups behave and interact. For instance, autocratic leaders make decisions unilaterally, which can stifle creativity and discourage team input. In contrast, democratic leaders encourage participation, empowering team members to share ideas and take ownership of their work.
A relatable example is how a coach's style can affect a sports team's performance. A coach who fosters collaboration and values each player's input often leads to a more engaged and motivated team. This principle applies equally in the workplace, where leadership can shape the culture and dynamics of a group.
The Importance of Communication
Effective communication is crucial for aligning team goals and fostering a culture of trust, which enhances productivity.
Ultimately, understanding different leadership styles allows organizations to choose leaders who align with their values and goals. This alignment can create a more harmonious and productive workplace.
Group Cohesion: The Glue That Holds Teams Together
Group cohesion refers to the bond that holds team members together, influencing their commitment and performance. High cohesion can lead to greater collaboration, while low cohesion may result in conflict and disengagement. It's the difference between a well-functioning team and one that struggles to work together.
Think of a close-knit family: they support each other, communicate effectively, and work toward common goals. Similarly, cohesive teams are more likely to share knowledge, provide support, and achieve their objectives. This sense of belonging is essential for fostering a positive work environment.
To build cohesion, organizations can encourage team-building activities and create opportunities for employees to connect on a personal level. By investing in relationships, businesses can enhance group dynamics and overall performance.
Conflict Resolution: Navigating Group Challenges
Conflict is a natural part of group interactions, but how it is managed can make all the difference. Effective conflict resolution strategies help teams navigate disagreements and maintain a positive working environment. This process often involves open communication and a willingness to understand different perspectives.
Imagine a group project where team members have differing opinions on the best approach. If they engage in constructive dialogue, they can reach a compromise that incorporates everyone's ideas. This not only resolves the conflict but also strengthens team bonds through collaboration.
Navigating Conflict for Growth
Implementing effective conflict resolution strategies allows teams to tackle disagreements constructively, strengthening their bonds.
Organizations can benefit from training employees in conflict resolution skills, equipping them to handle disputes amicably. By fostering a culture that views conflict as an opportunity for growth, businesses can enhance group dynamics and overall productivity.
The Future of Organizational Behavior in a Changing World
As workplaces evolve, so too does the study of organizational behavior. Factors like remote work and digital communication are reshaping group interactions, presenting new challenges and opportunities. Understanding these shifts is essential for organizations aiming to thrive in a competitive landscape.
For instance, remote teams must find innovative ways to foster connection and communication, often relying on technology to bridge gaps. This calls for a deeper understanding of how virtual interactions affect group dynamics and employee engagement.

Looking ahead, organizations that prioritize adaptability and continuous learning in their approach to organizational behavior will be better positioned to navigate future changes. By embracing new strategies, they can cultivate a resilient and engaged workforce.