Agile Methodology in Product Development: An Overview
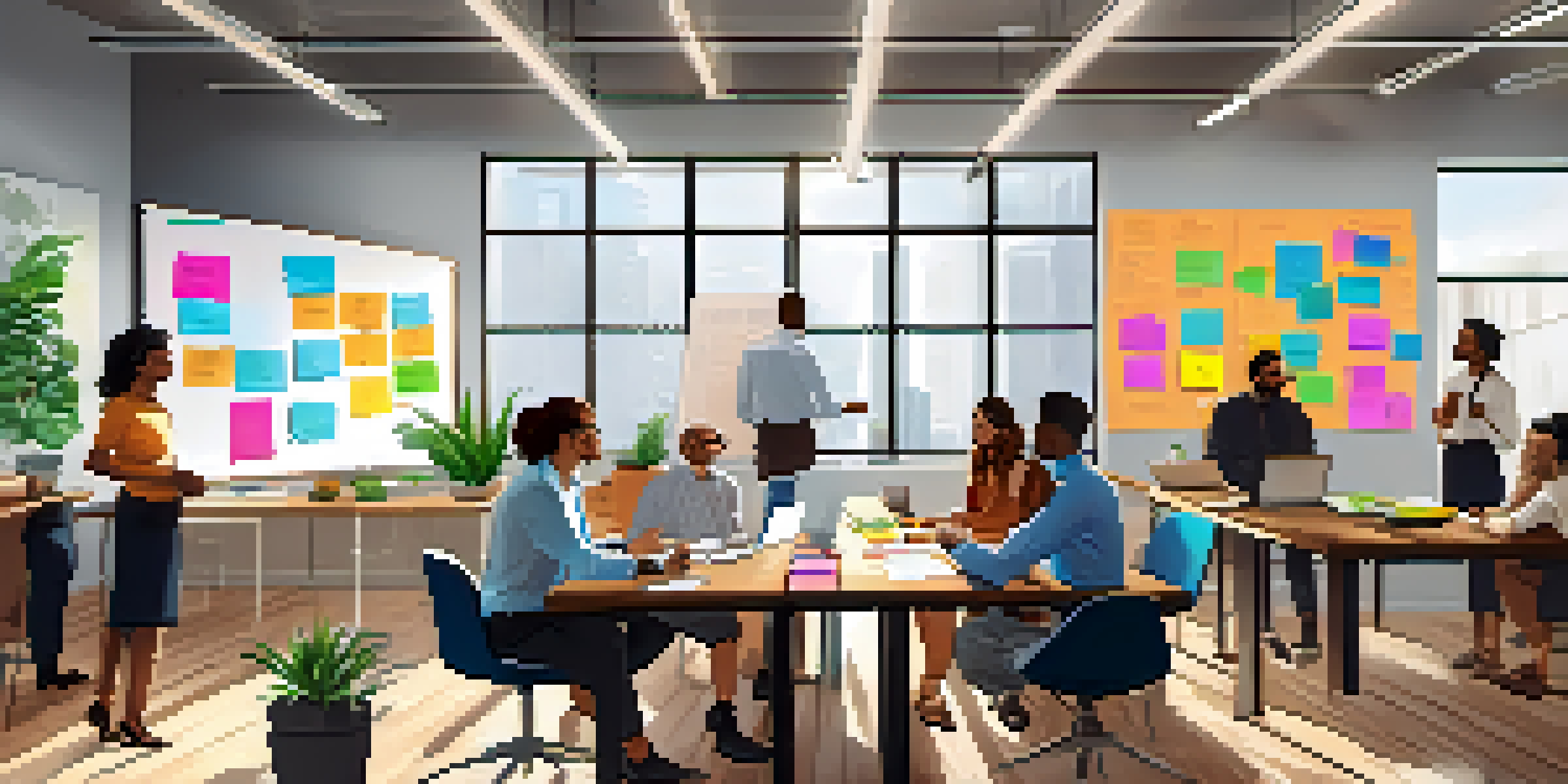

Understanding Agile Methodology and Its Origins
Agile methodology is a project management approach that emphasizes flexibility, collaboration, and customer feedback. It originated from the Agile Manifesto, created in 2001 by a group of software developers who sought to improve the way software was built. The core principles of Agile focus on delivering small, incremental updates rather than a single, complete product at once.
The only thing that matters is customer feedback and satisfaction, which drives the success of our product.
This iterative process allows teams to respond quickly to changes and incorporate user feedback continuously. For instance, instead of working for months on a project before revealing it to users, Agile teams release functional pieces regularly, allowing for adjustments based on real-world input. This adaptability is what sets Agile apart from traditional methodologies, which often follow a rigid, sequential path.
In short, Agile is all about embracing change and prioritizing customer satisfaction, making it particularly suitable for environments where user needs evolve rapidly. As we explore further, you’ll see how this methodology plays a crucial role in effective product development.
Key Principles of Agile Methodology
At the heart of Agile methodology are its key principles, which include customer collaboration, responding to change, and delivering working products frequently. These principles foster a dynamic environment where teams can iterate based on feedback. For example, rather than waiting until the end of a project to test a product, Agile encourages regular testing and adjustments throughout the development process.
Another principle is the emphasis on self-organizing teams. In Agile, team members are encouraged to take ownership of their work, which leads to increased motivation and accountability. This collaborative spirit not only enhances problem-solving but also builds a sense of trust and camaraderie among team members.
Agile Emphasizes Flexibility
Agile methodology prioritizes adaptability and customer feedback, allowing teams to respond swiftly to changing requirements.
Ultimately, these principles create a framework that prioritizes efficiency and quality, ensuring that the end product truly meets the needs of its users. This foundation is vital as we delve into the specific practices that embody Agile methodology.
Popular Agile Frameworks in Product Development
Several frameworks embody Agile principles, with Scrum and Kanban being among the most popular. Scrum is characterized by short, time-boxed iterations called sprints, typically lasting two to four weeks. During each sprint, teams focus on completing specific tasks that contribute to the project's overall goal, enabling rapid adjustments based on ongoing feedback.
Agile is not a destination, but a journey of continuous improvement and adaptation to change.
On the other hand, Kanban focuses on visualizing workflow to optimize efficiency. Teams use boards to track progress, allowing them to identify bottlenecks and adjust priorities as needed. This flexibility is particularly useful in environments where work items vary in size and complexity.
By understanding these frameworks, teams can choose the approach that best aligns with their project goals and team dynamics. Each framework offers unique benefits, making Agile adaptable to various contexts in product development.
The Role of the Product Owner in Agile
In Agile product development, the Product Owner plays a crucial role as the voice of the customer. This individual is responsible for defining the product vision and prioritizing the features that need to be developed. By maintaining a clear understanding of customer needs, the Product Owner ensures that the team is always focused on delivering maximum value.
Another key responsibility of the Product Owner is managing the product backlog, which is essentially a prioritized list of features and tasks. This backlog is continuously refined based on feedback and changing requirements, allowing for a flexible approach to development. Regular interactions with stakeholders also help the Product Owner make informed decisions about what to prioritize next.
Key Agile Frameworks Explored
Frameworks like Scrum and Kanban help teams implement Agile principles effectively, optimizing workflow and productivity.
In essence, the Product Owner acts as a bridge between the development team and the customer, facilitating communication and ensuring that the final product aligns with user expectations. This role is vital to the success of Agile methodologies and overall product development.
Agile Ceremonies: Keeping Teams Aligned
Agile methodologies incorporate specific ceremonies, or meetings, that help teams stay aligned and focused. Key ceremonies include sprint planning, daily stand-ups, sprint reviews, and retrospectives. Each of these meetings serves a distinct purpose and fosters collaboration among team members.
For instance, during sprint planning, the team discusses what they aim to accomplish in the upcoming sprint and assigns tasks accordingly. Daily stand-ups are short meetings where team members share their progress and any challenges they face, promoting transparency and quick problem-solving. At the end of each sprint, the team conducts a sprint review to showcase completed work and gather feedback.
Finally, retrospectives allow the team to reflect on their process and identify areas for improvement. By regularly engaging in these ceremonies, Agile teams can maintain momentum and continuously enhance their productivity, ultimately leading to better outcomes in product development.
Benefits of Agile Methodology in Product Development
The benefits of adopting Agile methodology in product development are numerous. One of the most significant advantages is increased flexibility, allowing teams to pivot quickly in response to changing market conditions or customer feedback. This adaptability can lead to higher customer satisfaction, as products are refined based on real user experiences and needs.
Additionally, Agile encourages faster delivery times by breaking projects into smaller, manageable increments. This means that teams can release functional features more frequently, which not only meets customer demands but also allows for earlier revenue generation. Companies that adopt Agile often find themselves with a competitive edge in the fast-paced market.
Product Owner's Vital Role
The Product Owner bridges the gap between the development team and customers, ensuring that the product aligns with user needs.
Moreover, Agile fosters a culture of collaboration and continuous improvement within teams. By emphasizing open communication and shared ownership, team members become more invested in the project's success, leading to greater innovation and creativity. Overall, these benefits make Agile an attractive choice for organizations looking to enhance their product development processes.
Challenges of Implementing Agile Methodology
Despite its many advantages, implementing Agile methodology can come with challenges. One common issue is resistance to change, particularly in organizations accustomed to traditional project management approaches. Team members may struggle to adapt to the new processes, leading to confusion and frustration during the transition.
Another challenge is maintaining consistent communication and collaboration, especially in remote or hybrid work environments. Agile relies heavily on face-to-face interactions, which can be difficult when team members are scattered across different locations. To counter this, teams must leverage technology effectively to ensure everyone stays connected and informed.

Finally, organizations may find it challenging to fully embrace the iterative nature of Agile, as they often want to see a complete product before making any changes. This desire for finality can hinder the flexibility that Agile promotes. By addressing these challenges head-on, teams can better position themselves for successful Agile adoption and reap the methodology's full benefits.